Subtitles & vocabulary
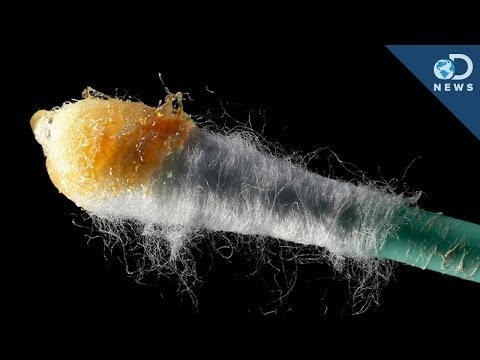
Why Do We Need Earwax?
00
Jack posted on 2015/11/26Save
Video vocabulary
stuff
US /stʌf/
・
UK /stʌf/
- Uncountable Noun
- Generic description for things, materials, objects
- Transitive Verb
- To push material inside something, with force
B1
More know
US /noʊ/
・
UK /nəʊ/
- Verb (Transitive/Intransitive)
- To be familiar with a person or place, thing
- To feel sure or be convinced about something
A1TOEIC
More gross
US /ɡros/
・
UK /ɡrəʊs/
- Noun (Countable/Uncountable)
- 144 of something; twelve dozen of something
- Total sum of money earned before costs and taxes
- Transitive Verb
- To earn an amount of money before costs and taxes
B1TOEIC
More Use Energy
Unlock Vocabulary
Unlock pronunciation, explanations, and filters
