Subtitles & vocabulary
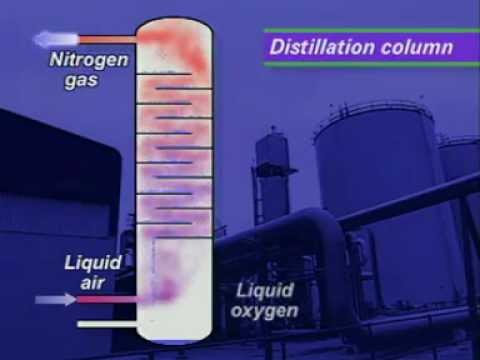
Gases from the Air
00
Yrchinese posted on 2017/02/04Save
Video vocabulary
process
US /ˈprɑsˌɛs, ˈproˌsɛs/
・
UK /prə'ses/
- Transitive Verb
- To organize and use data in a computer
- To deal with official forms in the way required
- Noun (Countable/Uncountable)
- Dealing with official forms in the way required
- Set of changes that occur slowly and naturally
A2TOEIC
More material
US /məˈtɪriəl/
・
UK /məˈtɪəriəl/
- Noun (Countable/Uncountable)
- Cloth; fabric
- Supplies or data needed to do a certain thing
- Adjective
- Relevant; (of evidence) important or significant
- Belonging to the world of physical things
A2
More eventually
US /ɪˈvɛntʃuəli/
・
UK /ɪˈventʃuəli/
- Adverb
- After a long time; after many attempts; in the end
- At some later time; in the future
A2
More filter
US /ˈfɪltɚ/
・
UK /'fɪltə(r)/
- Noun (Countable/Uncountable)
- Device to remove certain types of light, sound
- Device to remove unwanted things from liquid, gas
- Transitive Verb
- To remove certain types of light, sound
- To remove unwanted substances from a liquid or gas
B1
More Use Energy
Unlock Vocabulary
Unlock pronunciation, explanations, and filters
